Half-Cut Solar Panels- Key Advantages
- Hyde Source

- Jul 25, 2025
- 3 min read
Half-cut solar panels represent a significant evolution in photovoltaic (PV) technology, offering improved performance and durability compared to traditional "full-cell" panels.
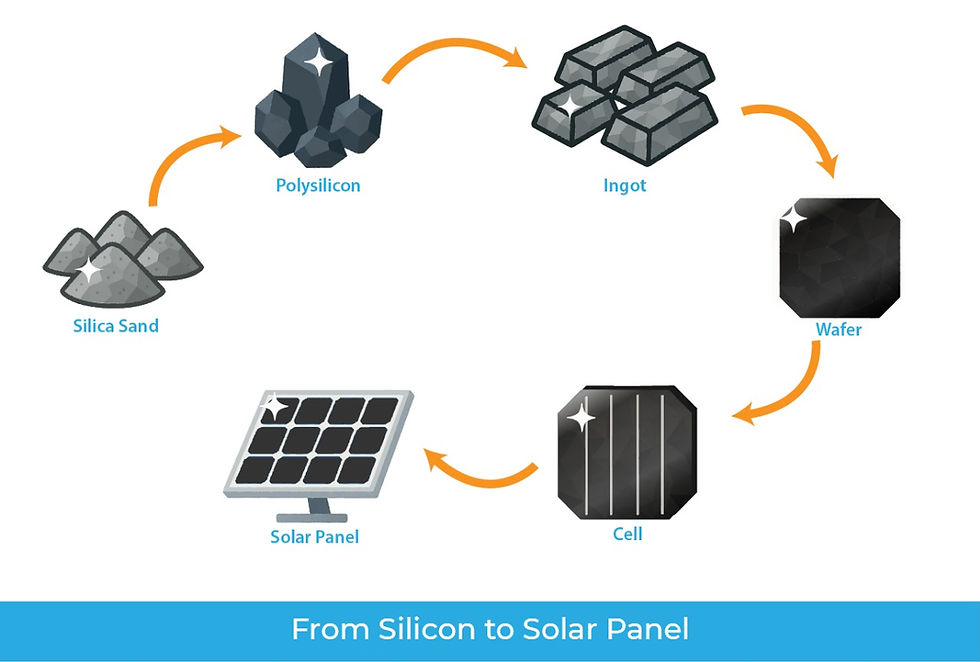
The core concept is simple: instead of using full-sized solar cells (typically 60 or 72 per panel), these cells are cut in half using a laser, effectively doubling the number of cells per panel (e.g., 120 or 144 half-cells in the same module footprint).
This seemingly small change in cell size leads to substantial benefits due to changes in how current flows and how the panel is wired.
What are Half-Cut Solar Panels?

In a traditional solar panel, full-sized solar cells (e.g., 156.75mm×156.75mm) are connected in series. When these cells are precisely cut in half (e.g., 156.75mm×78.375mm), the resulting "half-cut" cells produce half the current of a full cell, while maintaining the same voltage.
The panel itself is often divided into two independent halves (e.g., top and bottom sections), each acting as a smaller, independent array. This split design, combined with modified wiring (often doubling the number of strings/sub-strings), is key to their improved performance.
Pros of Half-Cut Solar Panels
Reduced Resistive Losses: This is the primary advantage. By cutting cells in half, the current flowing through each individual cell is halved. This directly translates to higher overall panel efficiency and more power output per square foot.
Improved Shading Performance: Half-cut panels are significantly more resilient to partial shading. Because the panel is often split into two independent sections and has more substrings, if one part is shaded, the other part can continue to generate power. In a traditional panel, shading just one cell can reduce the output of an entire string (e.g., 1/3rd of the panel's output). With half-cut cells, the impact is localized to a smaller section (e.g., 1/6th). This is particularly beneficial for urban rooftops or areas with unavoidable partial shading.
Lower Hot Spot Risk: Hotspots occur when shaded or faulty cells act as resistors, converting energy from other cells into heat. The reduced current in half-cut cells means less heat generated in such scenarios, lowering the risk of hot spot formation and potential long-term damage to the module.
Enhanced Durability: Smaller cells are inherently less susceptible to mechanical stress and micro-cracks during manufacturing, transport, installation, and throughout their operational life. This contributes to better long-term reliability and a longer lifespan for the panel.
Better Temperature Coefficient: Due to lower internal resistive losses, half-cut panels operate at slightly cooler temperatures. This means they perform better in hot climates like Bengaluru, where high temperatures can otherwise reduce solar panel efficiency.
Higher Power Output: Overall, half-cut panels deliver a higher power output (wattage) for the same module footprint compared to full-cell panels, making them ideal for installations with limited space.
Conclusion
Half-cut solar panel technology represents a significant leap forward in solar PV efficiency and reliability. While they might come with a slightly higher initial cost due to increased manufacturing complexity, their benefits, particularly in terms of reduced resistive losses, superior shading tolerance, lower hot spot risk, and enhanced durability, often outweigh this initial investment over the lifespan of a solar energy system.
For homeowners and businesses in regions like Bengaluru, where partial shading from trees or surrounding buildings can be a factor, or where high ambient temperatures are common, half-cut solar panels are an increasingly attractive choice for maximizing energy yield and ensuring a robust, long-lasting solar installation.