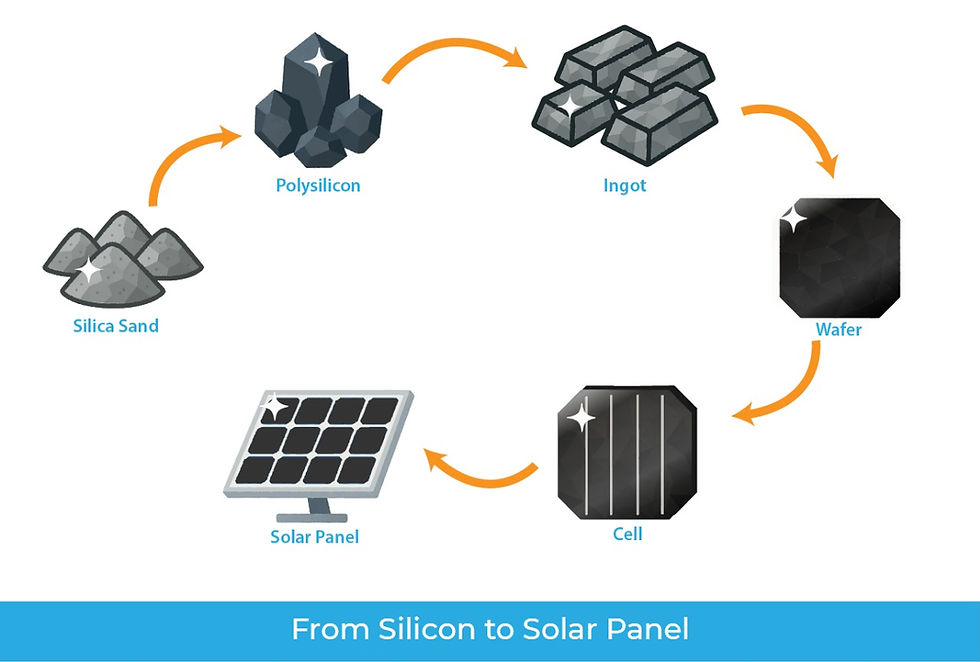
DC Junction Box: Design in Solar Power Plants
- Hyde Source

- Aug 1, 2025
- 3 min read
In the intricate architecture of a solar power plant, every component plays a vital role in converting sunlight into usable electricity. While solar panels capture the energy and inverters transform it, there's a critical, often overlooked, component that ensures the safe and efficient aggregation of power from multiple panels: the DC Junction Box, also commonly known as a Combiner Box.
Far from being a simple enclosure, a well-designed and correctly sized DC junction box is essential for protecting your solar investment, ensuring operational safety, and maximizing energy harvest. This blog post will delve into the crucial aspects of DC junction box design and sizing for solar power plants.
What is a DC Junction Box (Combiner Box)?
A DC Junction Box is an electrical enclosure that consolidates the direct current (DC) output from multiple solar panel strings into a single, larger DC output cable that then feeds into a central inverter. In essence, it acts as a central collection point for the DC power generated by the solar array.
The Critical Role of the DC Junction Box
The functions of a DC junction box extend far beyond mere wire management:
String Aggregation: It combines the current from several individual solar panel strings connected in parallel, allowing for a higher total current to be fed to the inverter.
Overcurrent Protection: It houses fuses or circuit breakers for each individual string, providing crucial protection against overcurrents that could damage panels or wiring in case of a fault.
Surge Protection: Many combiner boxes include Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) to safeguard the system from lightning strikes or other voltage surges.
Disconnect Means: Some boxes incorporate DC disconnect switches, allowing for safe isolation of the solar array from the inverter for maintenance or emergency purposes.
Key Design Considerations for DC Junction Boxes
Proper design ensures reliability and safety:
Safety First: The primary concern is protecting personnel and equipment. This includes robust overcurrent protection, proper grounding, and the ability to safely isolate the array.
Environmental Protection (IP Rating): Since combiner boxes are typically installed outdoors, they must have an adequate Ingress Protection (IP) rating (e.g., IP65, IP66, or IP67) to protect against dust, moisture, and water ingress.
UV Resistance: The enclosure and all internal components must be UV-resistant to withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight without degrading.
Temperature Management: The box must be designed to dissipate heat effectively, preventing internal components from overheating, especially in hot climates. Adequate ventilation or heat sinks might be required.
Accessibility & Maintenance: The internal layout should allow for easy access to fuses, circuit breakers, and terminals for inspection, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Material Selection: Enclosures are typically made from durable materials like polycarbonate, fiberglass, or painted steel, chosen for their weather resistance, strength, and non-conductivity (for non-metallic enclosures).
Components of a Typical DC Junction Box
A standard DC junction box typically includes:

Input Terminals (e.g., MC4 Connectors): For connecting the positive and negative cables from each solar string.
DC Fuses or Circuit Breakers: For overcurrent protection of individual strings.
Busbars: Copper or aluminum bars that combine the current from all protected strings into a single positive and negative output.
Surge Protection Devices (SPDs): To divert harmful voltage surges away from sensitive equipment.
Installation and Best Practices
Location: Install the combiner box as close as practically possible to the solar array to minimize DC cable runs and associated voltage drop.
Mounting: Securely mount the box on a stable, non-flammable surface, ensuring proper ventilation and protection from direct sunlight if possible.
Wiring: Use appropriate PV-rated cables, ensure proper crimping of terminals, and maintain neat, organized wiring to prevent hot spots and facilitate troubleshooting.
Grounding: The combiner box enclosure and any metallic components must be properly grounded according to electrical codes to ensure safety.
Labeling: Clearly label all strings, fuses, and disconnects for easy identification and safe operation.
Conclusion
The DC junction box, or combiner box, is a cornerstone of solar power plant design, ensuring the safe, efficient, and reliable aggregation of power from your solar array. Its proper design and meticulous sizing, considering factors like current, voltage, environmental conditions, and safety standards, are non-negotiable for maximizing energy yield and protecting your investment.
Ready to go solar? We're here to help! Reach out to our experts today for a personalized discussion about your specific requirements. We'll craft the ideal solar system that perfectly fits your needs and budget.